View this notebook on GitHub or run it yourself on Binder!
Integrate with Git¶
rubicon_ml’s git integration allows you to automatically track relevant version control information like branches and commits during your model iteration process. Use this integration when you are developing within a git repository to seamlessly tie your rubicon_ml experiments directly to the model code that produced them - an audit and governance must have!
To enable this feature, instantiate the rubicon_ml object with auto_git_enabled=True.
[1]:
from rubicon_ml import Rubicon
rubicon = Rubicon(persistence="memory", auto_git_enabled=True)
Any project created with this client will have the URL of the GitHub repo’s origin automatically populated in the github_url property.
[2]:
project = rubicon.create_project("Automatic Git Integration")
project.github_url
[2]:
'https://github.com/capitalone/rubicon-ml.git'
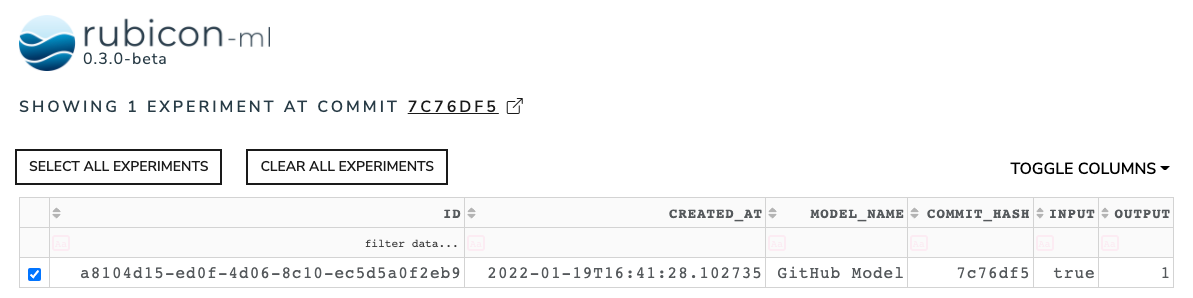
Experiments will have the current active branch name and last commit hash populated in the branch_name and commit_hash fields, respectively.
[3]:
experiment = project.log_experiment(model_name="GitHub Model")
experiment.branch_name, experiment.commit_hash
[3]:
('rubicon-ml', '7c76df58384ee03f231521e247b351386f8b3cd1')
These properties can help easily associate projects and experiments with the exact branches and commits they were run against so we can go back and reference the code later.
[4]:
from rubicon_ml.viz import Dashboard
experiment.log_parameter(name="input", value=True)
experiment.log_metric(name="output", value=1.0)
Dashboard([experiment]).show()
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:8050/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
127.0.0.1 - - [14/May/2021 11:58:45] "GET /_alive_e9483f78-700c-4852-a59e-f027a3b5caf7 HTTP/1.1" 200 -
Dash app running on http://127.0.0.1:8050/
Within the rubicon_ml dashboard, your experiments will be grouped by commit hash, which will link directly to the commit on GitHub.